Elasticy: A Dynamic Runtime-Reconfigurable Dataflow Accelerator
People: Konstantin Hossfeld, Nathan Sobotka (equal contribution)
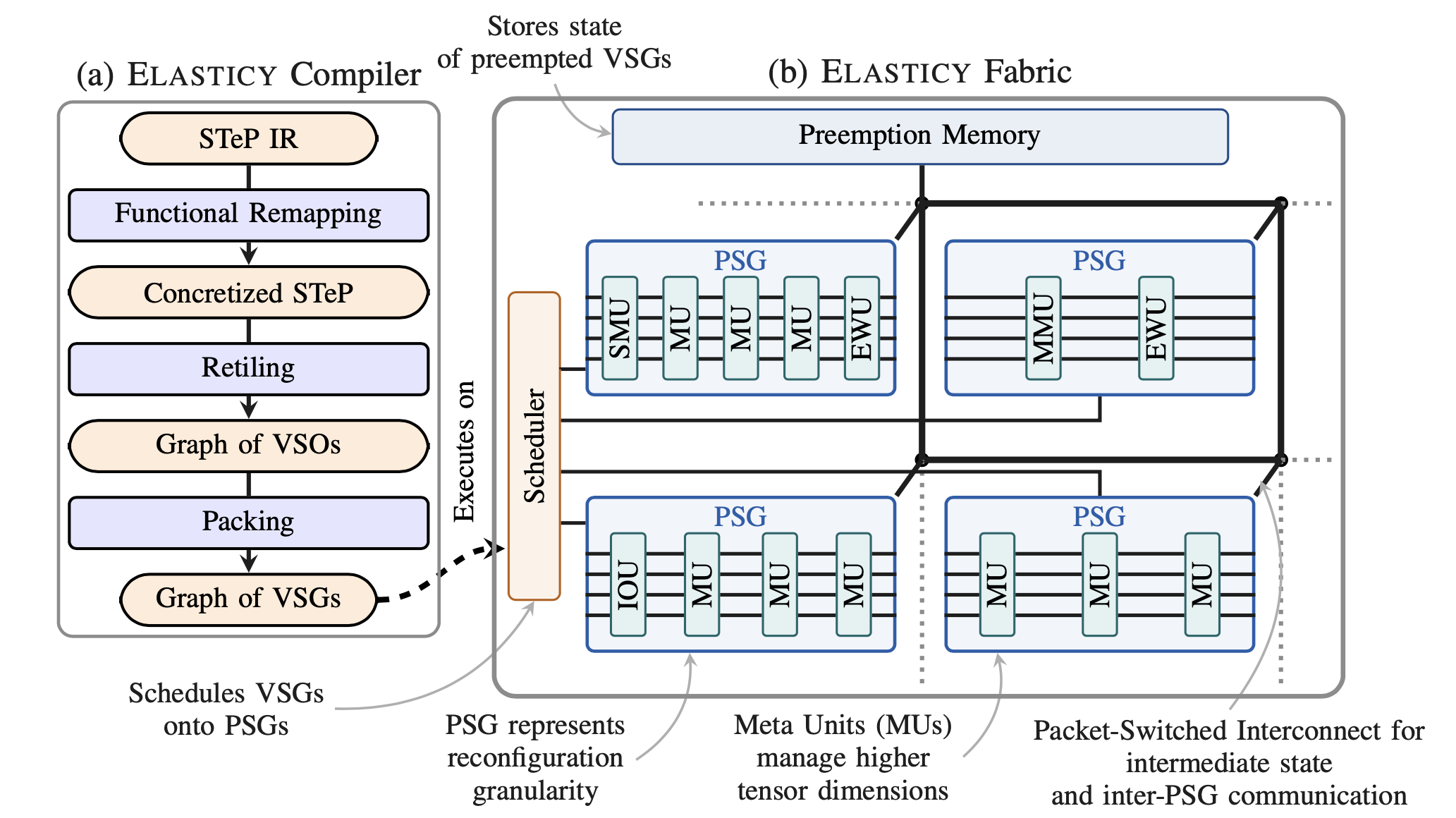
Recent data-intensive workloads have been expressing growing degrees of data-dependent dynamism. This includes, but is not limited to, state-of-the-art large language models, which increasingly use mixture-of-experts models to scale without a proportional increase in computation. Prior systems, including GPUs and reconfigurable dataflow accelerators (RDAs), struggle to exploit this dynamism efficiently, resulting in added memory traffic and compute underutilization due to extensive use of padding, predication and kernel-by-kernel execution. This problem exists throughout the stack: Program representations and compilers fail to preserve dynamic program characteristics, and state-of-the-art hardware cannot exploit it. To address this gap, we are developing a novel dynamic software stack, consisting of a dynamic tensor streaming programs IR (STeP) and Elasticy, a compiler and fabric designed for high dynamic workload performance.
The Elasticy Fabric executes dynamic applications spatially in a dataflow fashion. To support the types of dynamism present in recent workloads, Elasticy includes a novel runtime scheduler designed to maximize utilization of the fabric, a memory system that handles unbounded and dynamically sized tensors, and special compute units to support the dynamic tensor operations expressed in STeP without concretizing the dynamic dimensions.
Elasticy comes with full compiler support so that programs expressed in STeP can be executed on the fabric.